What Are Flat Feet?
The term flat feet describes fallen arches in which the arches of the foot flatten, leaving the whole sole in near complete contact with the ground. This is important because it highlights a low or non-existent foot arch, which can lead to misalignment, stress on other joints, and foot problems. The medical term for flat feet is ‘pes planus,’ which is also the correct medical term for fallen arches.
The foot is the foundation of the whole body. So fallen arches can misalign the feet, potentially leading to further complications. Flat feet are common, particularly in Asian populations (affecting roughly 1 in 5 people), and are often benign. Many people never require care until symptoms develop. Generalised ligament laxity or hypermobility can predispose to flexible flat feet, and prolonged use of complex, artificial walking surfaces can aggravate symptoms over prolonged periods of time.
Flat feet can occur from birth or develop over time due to wear and tear on the ligaments and tendons supporting the arch. Developing flat feet can also be influenced by hereditary factors, muscle or ligament issues, and poor footwear choices.
While many with flat feet have no discomfort, others may experience pain, instability, or alignment problems in the knees, hips, lower limbs, and lower back. Even if they cause no problems now, they may cause problems in future. That’s why podiatry flat-foot specialists recommend a consultation if you have flat feet.
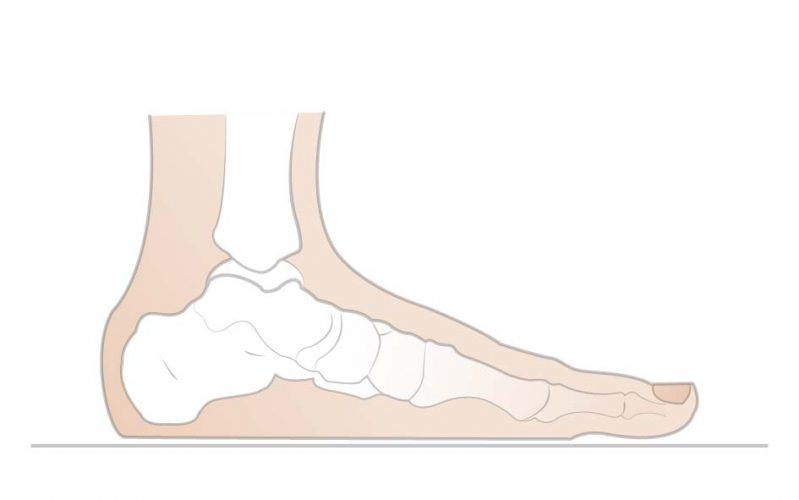
Types of Flat Feet
Flat feet types can also be classified into several categories:
- Flexible flat feet have an arch when seated or on tiptoes, but disappear when weight-bearing and standing. This type is often seen in children and can persist into adulthood, sometimes causing discomfort or instability. If the arch flattens but reappears on tiptoe, it’s likely flexible flat feet.
- Rigid flat feet have no visible arch, regardless of movement or weight bearing. Rigid flat feet are less common but more severe. The foot is stiff, and toe movement can be limited, often leading to significant pain or difficulty with daily activities. Rigid flat feet may be associated with underlying conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, or with prior foot or ankle injuries.
- Congenital flat feet or congenital flat foot are present from birth. Some children are born with flat arches that may or may not develop arches as they grow. If the arch does not form and symptoms such as pain or difficulty walking occur when the child stands, early intervention and treatment are recommended.
- Adult-acquired flat feet or adult acquired flat feet develop later in life, often due to wear and tear, injury, or medical conditions that affect the tendons and ligaments supporting the foot arch. This type can progress gradually through more advanced stages.
There is no blanket flat foot treatment or blanket treatment. Management should be tailored to the individual patient’s specific condition and presentation. Understanding the different types of flat feet is key to finding the proper treatment and support. If pain limits activity, swelling persists beyond 2 weeks, or you notice a progressive change in foot shape or balance, it’s wise to book a podiatry assessment at a flatfoot clinic.
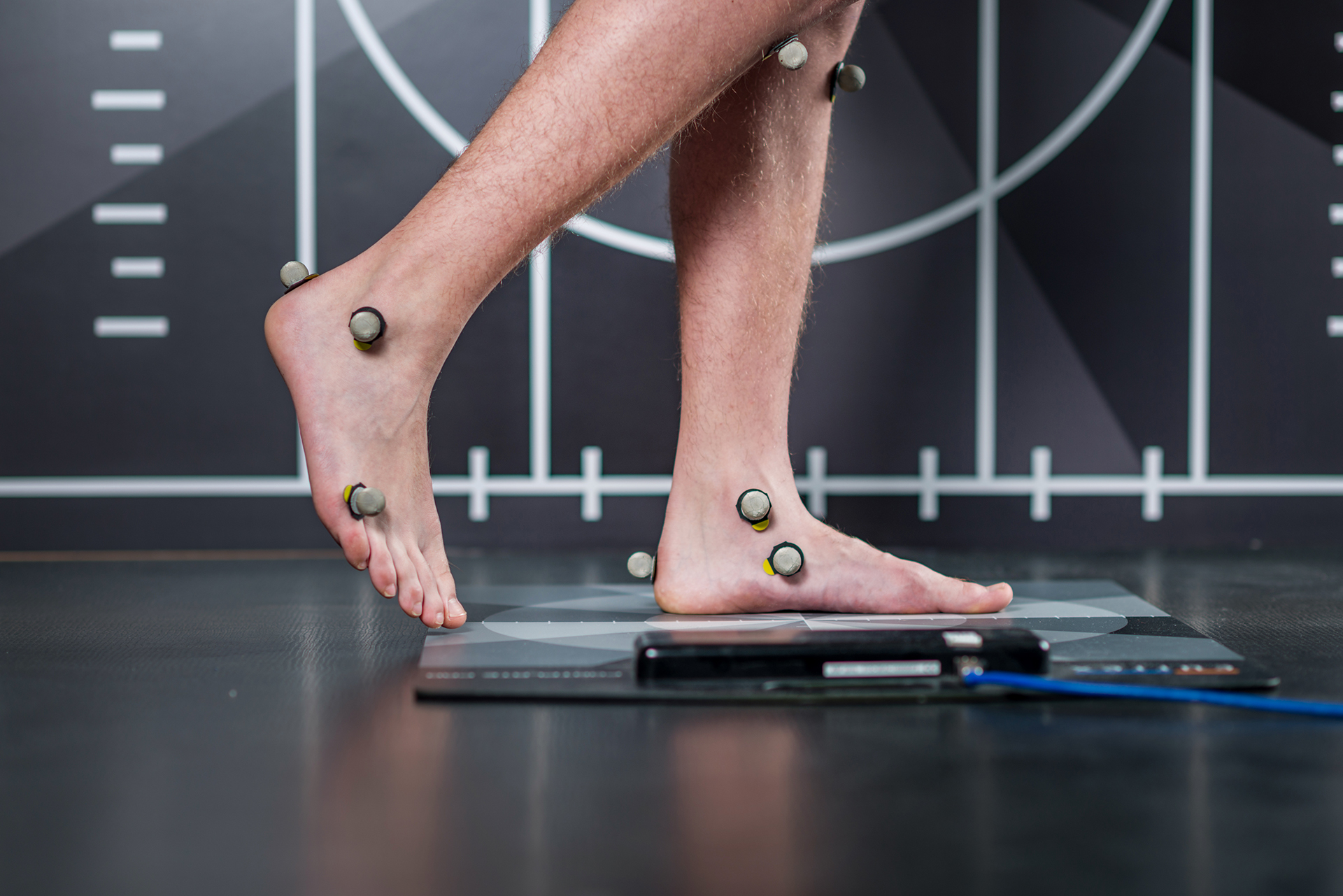

Foot Arches and Support
The foot arch is a vital primary support structure that distributes your body’s weight and helps absorb the impact of movement. A normal arch distributes pressure evenly across the foot, reducing the risk of foot and ankle injuries and supporting healthy movement. When the arch collapses, resulting in fallen arches or flat feet, the entire sole comes into near-complete contact with the ground.
The inner side of the foot, where the arch is located, often bears the brunt of this strain, leading to discomfort and, in some cases, swelling. Over time, the lack of proper arch supports can contribute to further issues, including ankle injuries and even problems in the knees or lower limbs.
Addressing flat feet early is crucial to avoid severe pain and long-term complications. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional or sports medicine specialist can help monitor your foot health, recommend appropriate insoles and orthotic devices, and guide you through stretching exercises and exercises to maintain a healthy, functional arch. By taking proactive early treatments, you can reduce discomfort, support your feet, and lower the risk of future injuries.

Flat Feet Symptoms, Foot Pain and Diagnosis
Not everyone with flat feet has symptoms. However, when discomfort occurs, it’s usually felt in the arch, the heel, or the inner ankle. Other common flat foot symptoms include swelling on the inner side of the foot, foot pain that worsens with prolonged standing or walking, and discomfort radiating up the legs.
From a biomechanical perspective, excessive inward rolling or excessive subtalar pronation of the heel and midfoot is common. You may notice an outward heel tilt, a collapsed inner arch on standing, when flat feet stand, or uneven shoe wear along the inner edge. Many with flat feet often describe tired or aching feet, especially after activity, and individuals with flat feet may develop tired or sore feet after prolonged standing or walking. Leg cramps at night or a feeling of walking on the inner edge of the foot are also common.
When visiting a flat foot clinic for flat foot assessment, difficulty or pain on a single-leg heel-rise test can suggest posterior tibial tendon dysfunction, and a ‘too-many-toes’ sign viewed from behind indicates hindfoot valgus.

Management of Flat Feet
Footwear and Orthotic Support
Choosing the proper footwear is essential for flat feet. Flat-foot shoes should offer good arch support and cushioning to distribute pressure evenly. Custom orthoses tailored to an individual’s foot shape help align the foot and prevent foot pain. Unlike generic insoles, custom-made orthotic devices are tailored to support biomechanical function and reduce stress on the arch and surrounding joints.
For shoes for flat feet in Singapore, look for a firm heel counter, midfoot torsional stiffness and a moderate rocker or posting to limit over-pronation. Avoid very flexible uppers or long-term high heels that restrict toe movement. In some cases with significant instability or fatigue, an ankle-foot orthosis (AFO) may be considered short-term to support alignment while symptoms settle and strength improves.
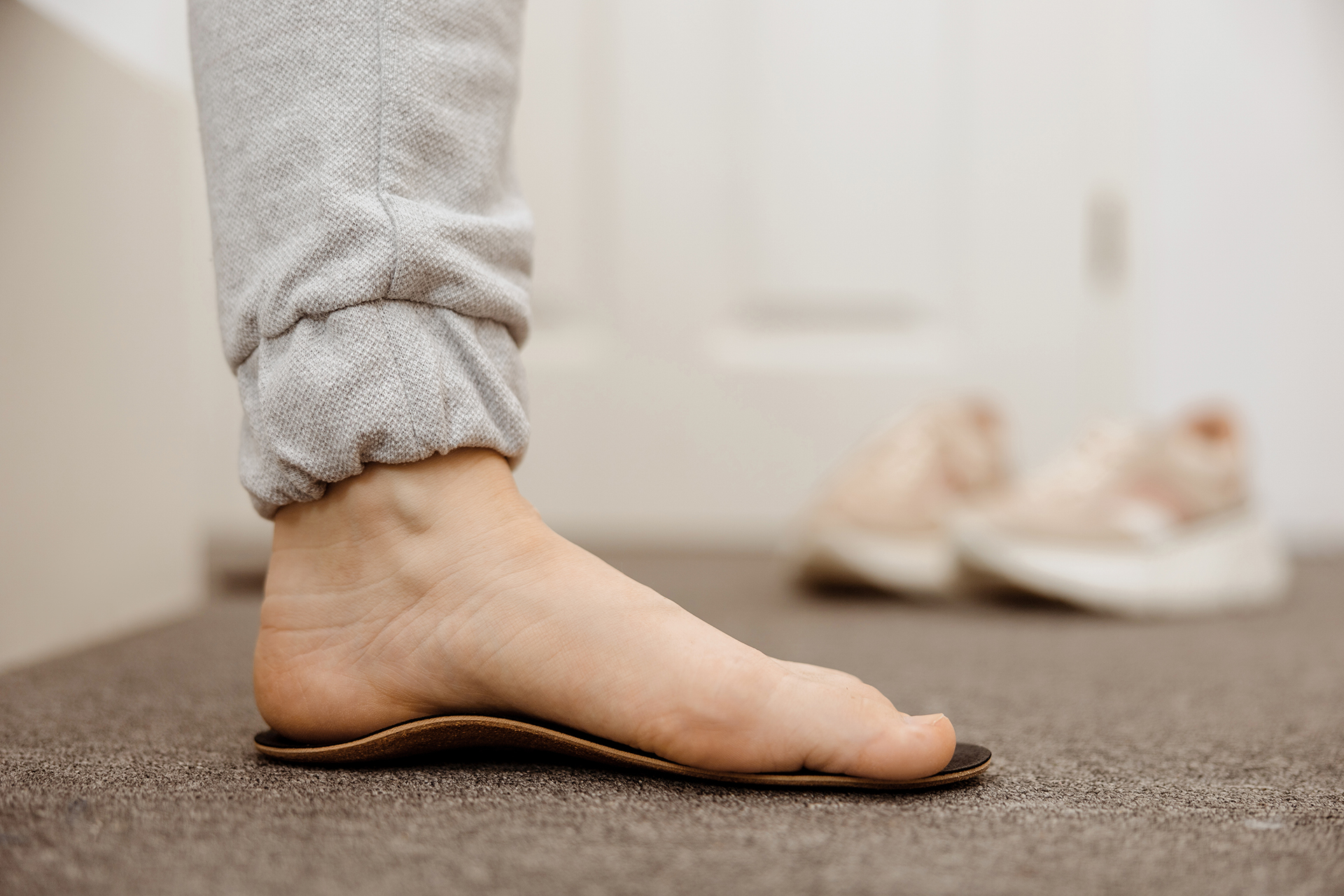

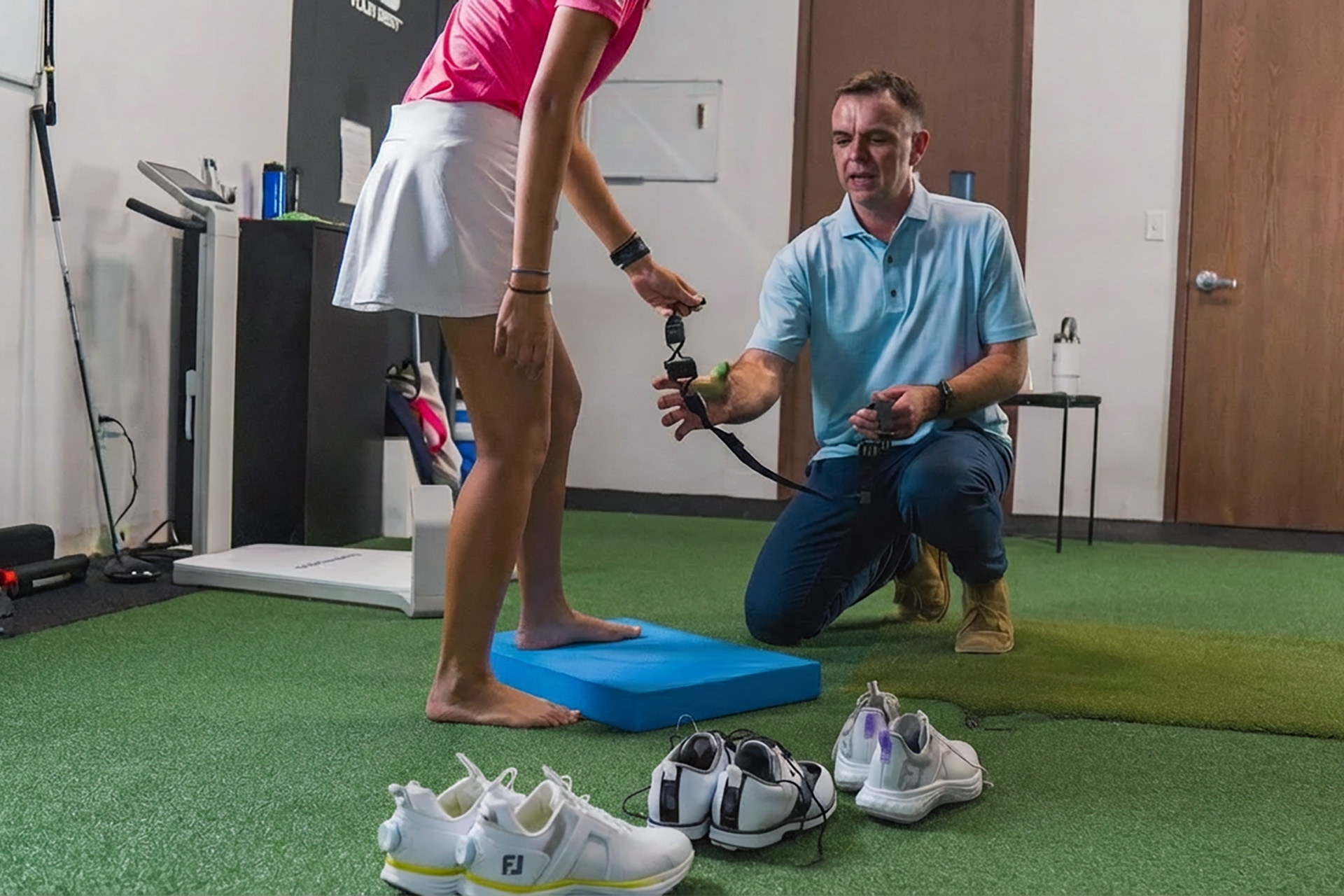
3D Infrared Gait Analysis for Movement Optimisation
3D Infrared Gait Analysis is a detailed assessment of walking and running patterns for those with recurring pain or fatigue due to flat feet. This technology enables podiatrists to identify movement inefficiencies and deliver precise interventions tailored to each patient’s biomechanics. By analysing foot pressure distribution, gait cycle abnormalities and postural imbalances, podiatrists can help you improve efficiency and comfort, especially for athletes in sports medicine.
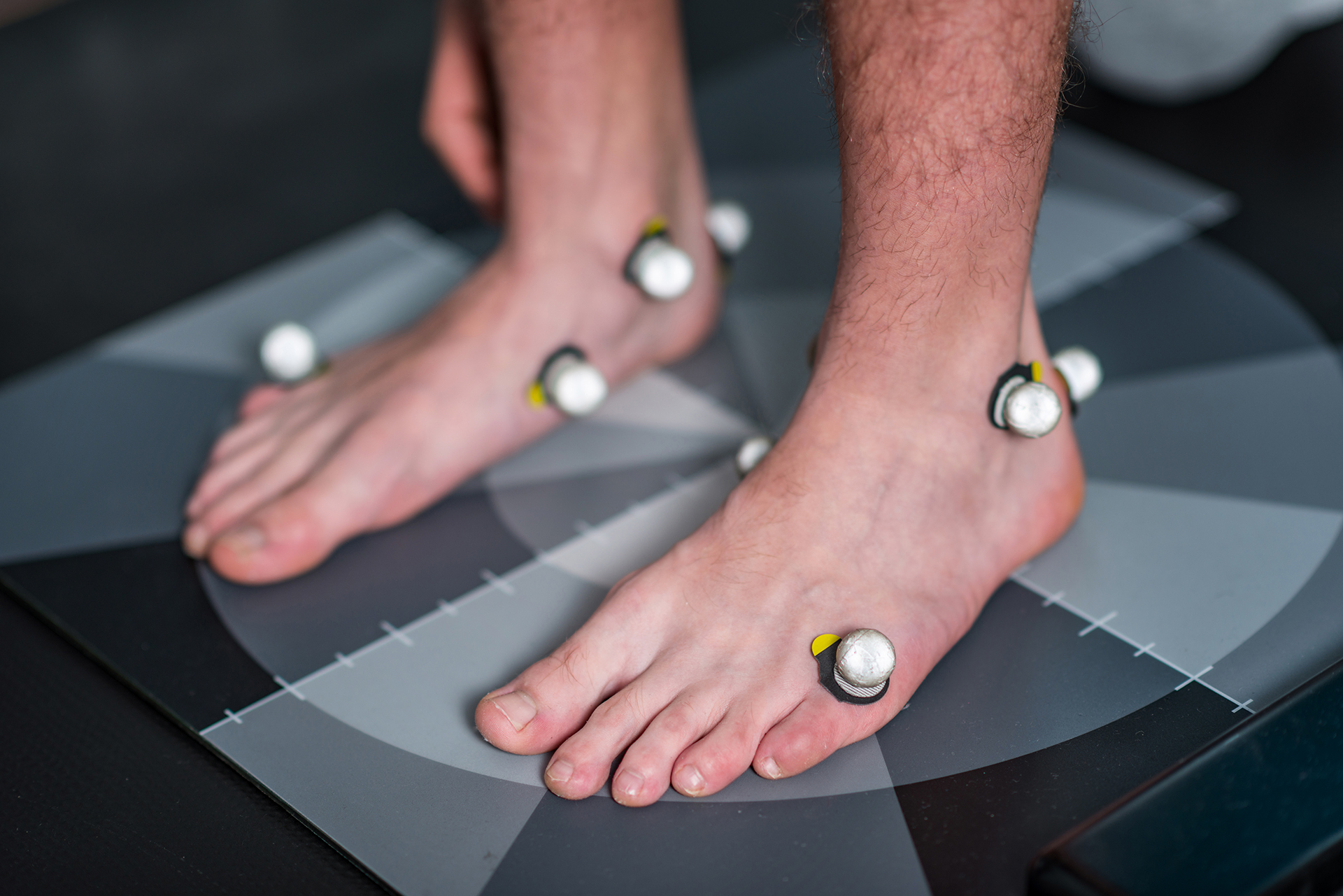
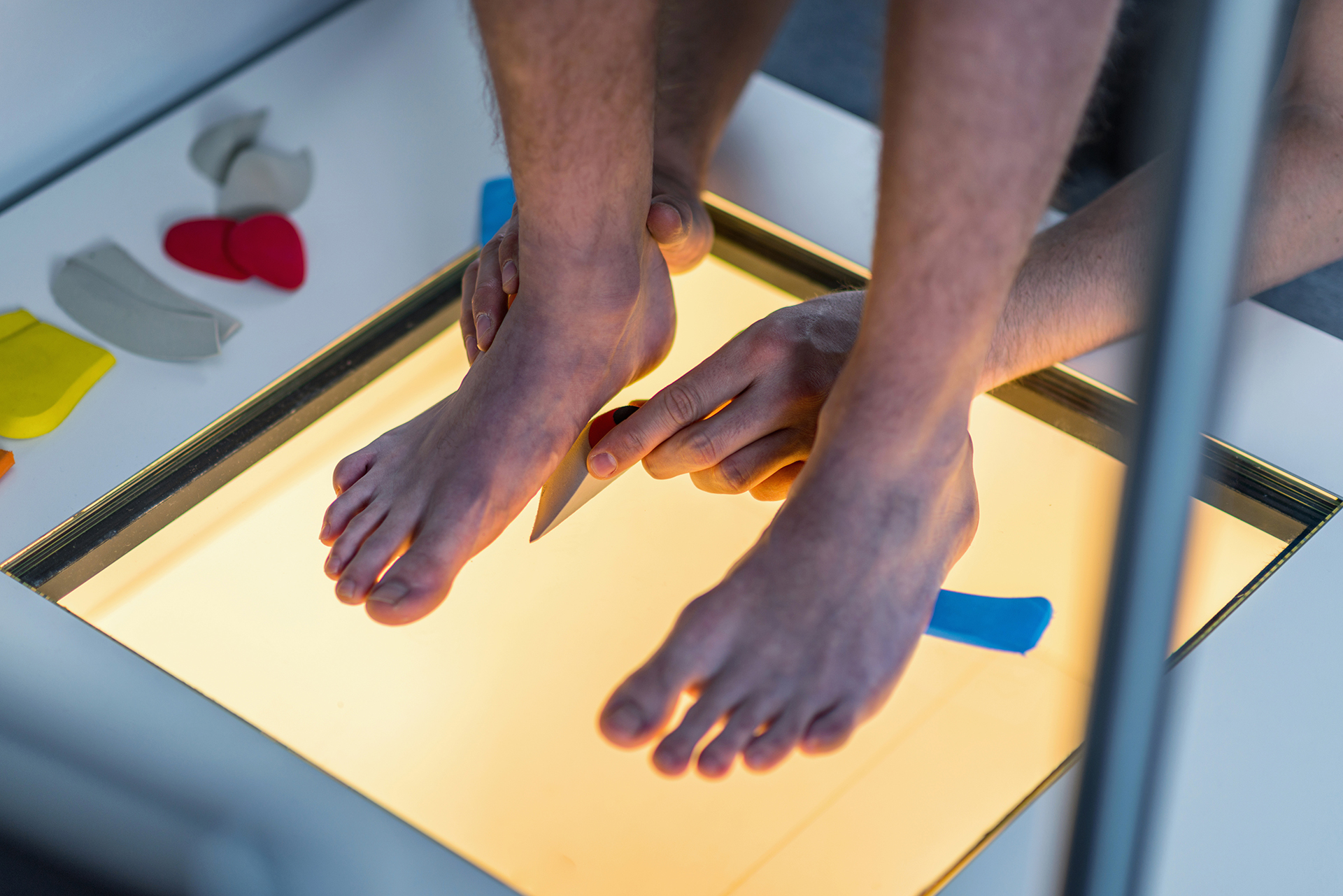
RehaWalk® for Gait Rehabilitation
One of the latest innovations in podiatric care, the RehaWalk pressure-sensor treadmill is a game-changer for gait retraining. RehaWalk helps individuals with flat feet to achieve proper foot function and weight distribution by providing real-time feedback and biomechanical adjustments. This is especially useful for those with difficulty walking, balance issues, or recurring injuries due to poor foot posture and flatfoot deformity.

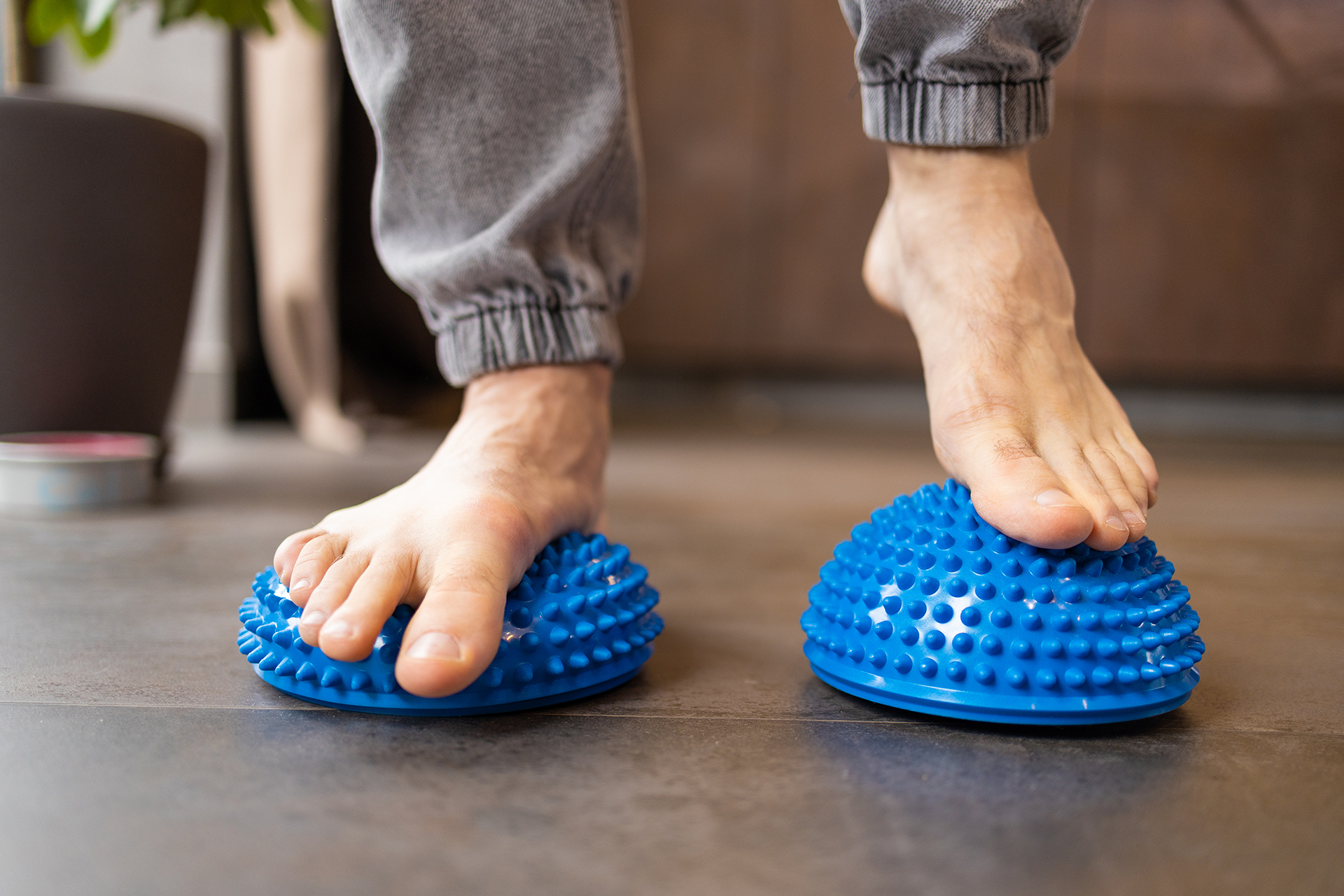
Exercise and Strengthening Programs
A structured exercise program can help manage flat feet by strengthening the foot’s intrinsic muscles and stretching the Achilles tendon and calf muscles. It is also important to include stretching exercises, including calf stretches targeting the posterior calf muscles, as this can improve foot alignment and help manage flat feet. Arch lifts, towel curls and marble pickups are other exercises that can help strengthen the arches of the feet. A podiatrist flat feet specialist can guide patients through customised mobility exercises to improve foot strength and flexibility, reduce pain and fatigue, and, during flare-ups, progressively modify activities through physical therapy.

When to Have Surgery for Rigid Flat Feet?
For most, conservative measures and conservative management, such as footwear adjustments, orthotic support, and gait rehabilitation, will resolve flat-foot symptoms. However, in severe cases of pain when conservative treatment fails, flatfoot surgery may be recommended by orthopaedic surgeons.
When conservative flatfoot treatment in Singapore fails, various surgical procedures may be recommended to restore foot mechanics and relieve pain. The choice of surgical procedure, such as tendon reconstruction, osteotomy (including Achilles tendon calcaneal osteotomy) or fusion surgery, will depend on the patient’s specific condition. Further details on surgical options are available during consultation.
Why Choose a Podiatrist for Flat Feet?
Our podiatrists at The Foot Practice focus on the biomechanics of the feet and offer non-surgical interventions and rehabilitation programmes to restore optimal function and long-term pain relief.
If you’re experiencing discomfort due to flat feet, don’t wait for it to worsen. Whether you need flat-foot shoes in Singapore, custom orthotics, or advanced gait rehabilitation, The Foot Practice provides comprehensive management for your foot condition. Early management improves mobility, reduces pain and prevents future complications. Contact us today if you have flat feet and would like an initial consultation with our leading podiatrist.